Guidelines for ESD Protection
Electrostatic Discharge
What is Static Electricity?
Static electricity is an electrical charge at rest created mainly by friction and separation causing an imbalance of electrons. The magnitude of the static electricity depends greatly on the type of materials, speed of separation, contact pressure, relative humidity of the environment, etc.
What is Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)?
It is the sudden transfer (discharge) of static electricity from one subject to another. It is a micropark.
What problems Static Charges have to all of us?
In our daily activities, a person may feel a shock if the electrostatic discharge is 3,000 volts or more. However, modern electronic components such as IC chips cannot even withstand charges of less than 500 volts causing it to be damaged without us noticing or realising the consequences. As technology is fast catching up, an electronics component becomes even more sensitive to the slightest amount of electrostatic discharge.
This have led us to realised how critical ESD is to us in our modern society causing many Companies' to invest substantially in such critical area to protect the sensitive components.
How static charge is generated?
Triboelectrification
Is the charge that generated when two kind of materials come into contact and then separated. These two objects become charged by gained electrons from the other. The magnitude and polarity of charges depends upon the characteristics of the two materials and affected by several factors like surface condition, size of contact area, speed of separation and humidity.
Field Induction
Static charge on an object create an electrostatic field that extend to surrounding can induce the charge on the objects that place nearby and caused them to become charged. Once it come to contact to the ungrounded ESD sensitive devices, the amount of unbalance charges will immediately transfer whice cause the device damage permanently.
What are the Solutions to ESD?
Virtually it is impossible to completely eliminate ESD in the production environment. We can minimise the problem by:-
Grounding
This eliminates static charges in building up rapidly. Grounding drains all static charge built up instantly, making it the most common option used in the electronic industry. Grounding includes personnel grounding devices such as wrist straps and workstation grounding devices such as ESD chair.
Neutralisation
This method eliminates static charges through ionization. In this method, ions are created artificially to neutralise charges on both insulators and isolated conductors. However, neutralisation thorgh ionization should go parallel with grounding as it only reduces the probability of an ESD event occurring.
Protection
Protect by isolating electronics components from charged objects, fields, and insulator transportation. Using the Faraday Cage concept, this concept emphasize that static charges cannot penetrate conductive materials.
Prevention
The best solution to an ESD problem is prevention and only you can prevent this from happening. The person in charge should be aware of events ESD could happen, understand the application of ESD and ensure ESD DOES NOT happen. Training should be carried out to ensure everyone is knowledgeable of ESD awareness in ESD - sensitive areas followed by enforcement.
However, the ultimate responsibility lies with everyone and this makes everything possible.
What is Static Electricity?
Static electricity is an electrical charge at rest created mainly by friction and separation causing an imbalance of electrons. The magnitude of the static electricity depends greatly on the type of materials, speed of separation, contact pressure, relative humidity of the environment, etc.
What is Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)?
It is the sudden transfer (discharge) of static electricity from one subject to another. It is a micropark.
What problems Static Charges have to all of us?
In our daily activities, a person may feel a shock if the electrostatic discharge is 3,000 volts or more. However, modern electronic components such as IC chips cannot even withstand charges of less than 500 volts causing it to be damaged without us noticing or realising the consequences. As technology is fast catching up, an electronics component becomes even more sensitive to the slightest amount of electrostatic discharge.
This have led us to realised how critical ESD is to us in our modern society causing many Companies' to invest substantially in such critical area to protect the sensitive components.
How static charge is generated?
Triboelectrification
Is the charge that generated when two kind of materials come into contact and then separated. These two objects become charged by gained electrons from the other. The magnitude and polarity of charges depends upon the characteristics of the two materials and affected by several factors like surface condition, size of contact area, speed of separation and humidity.
Field Induction
Static charge on an object create an electrostatic field that extend to surrounding can induce the charge on the objects that place nearby and caused them to become charged. Once it come to contact to the ungrounded ESD sensitive devices, the amount of unbalance charges will immediately transfer whice cause the device damage permanently.
What are the Solutions to ESD?
Virtually it is impossible to completely eliminate ESD in the production environment. We can minimise the problem by:-
Grounding
This eliminates static charges in building up rapidly. Grounding drains all static charge built up instantly, making it the most common option used in the electronic industry. Grounding includes personnel grounding devices such as wrist straps and workstation grounding devices such as ESD chair.
Neutralisation
This method eliminates static charges through ionization. In this method, ions are created artificially to neutralise charges on both insulators and isolated conductors. However, neutralisation thorgh ionization should go parallel with grounding as it only reduces the probability of an ESD event occurring.
Protection
Protect by isolating electronics components from charged objects, fields, and insulator transportation. Using the Faraday Cage concept, this concept emphasize that static charges cannot penetrate conductive materials.
Prevention
The best solution to an ESD problem is prevention and only you can prevent this from happening. The person in charge should be aware of events ESD could happen, understand the application of ESD and ensure ESD DOES NOT happen. Training should be carried out to ensure everyone is knowledgeable of ESD awareness in ESD - sensitive areas followed by enforcement.
However, the ultimate responsibility lies with everyone and this makes everything possible.
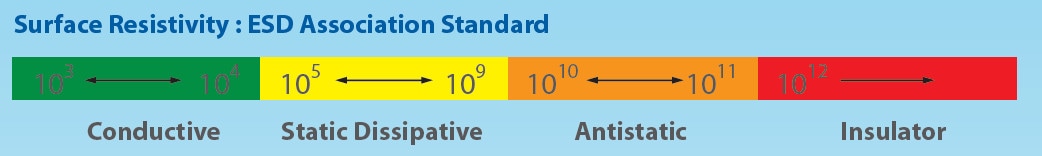
ESD Material Classification
1. Conductive : good shielding, allows charges to drain quickly,
eliminates charges buildup.
2. Static Dissipative : drains a charge to ground moderately,
minimal shielding, minimizes charge buildup
3. Antistatic : minimizes charge buildup up via triboelectricity.
1. Conductive : good shielding, allows charges to drain quickly,
eliminates charges buildup.
2. Static Dissipative : drains a charge to ground moderately,
minimal shielding, minimizes charge buildup
3. Antistatic : minimizes charge buildup up via triboelectricity.
Surface Resistivity : ESD Association Standard
Static Electricity always exists
In today's workplace, the life and reliability of modern semiconductors require an environment where static electricity is continuously and totally drained to ground. Therefore, an Electrostatic Protected Area (E.P.A) must be established at all stages of receipt, storage, assembly test and transport of electronic devices.
In today's workplace, the life and reliability of modern semiconductors require an environment where static electricity is continuously and totally drained to ground. Therefore, an Electrostatic Protected Area (E.P.A) must be established at all stages of receipt, storage, assembly test and transport of electronic devices.
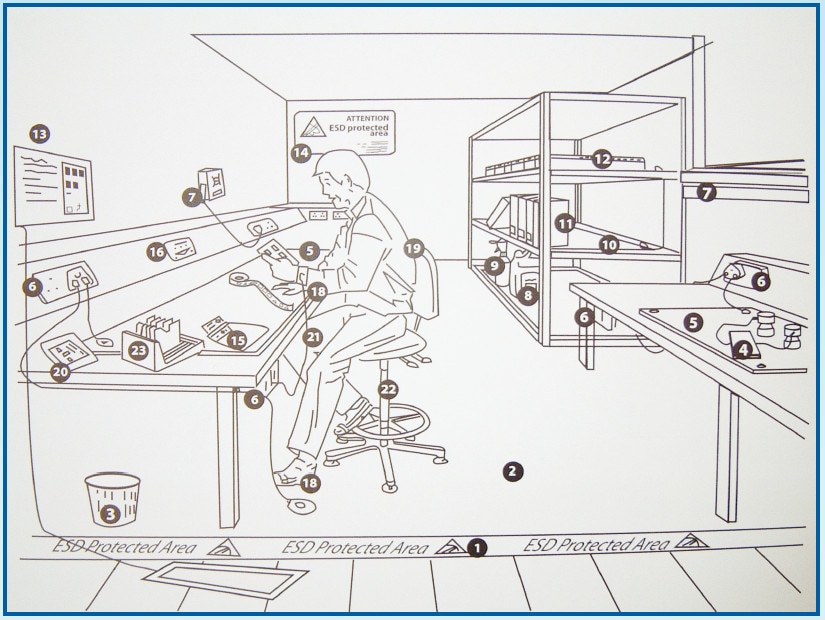
1. Boundaries : Cleary mark & identify the visible boundaries of your EPA for all to see
2. Clearing : Ban all static generating materials from entering your EPA
3. Grounding : All workstation & surfaces must be properly grounded in your EPA
4. Presonnel : All working personnel and visitors must be properly grounded in your EPA
5. Handling & transportation : Protect your components with ESD safe materials
6. Training & awareness : Ensure that all personnels are properly trained aware at all aspects of static protection.
2. Clearing : Ban all static generating materials from entering your EPA
3. Grounding : All workstation & surfaces must be properly grounded in your EPA
4. Presonnel : All working personnel and visitors must be properly grounded in your EPA
5. Handling & transportation : Protect your components with ESD safe materials
6. Training & awareness : Ensure that all personnels are properly trained aware at all aspects of static protection.
|
1. Floor marketing tape
2. Flooring 3. Waste basket 4. Meters and probes 5. Bench mat 6. Earth bonding points and earth facility 7. Ionisers 8. Floor polish 9. Bench top Cleaner 10. Shelving 11. Ring binders 12. Shipping tube holders 13. Footwear tester 14. Signs 15. Labels and tapes 16. On-demand wrist strap testers 18. Wrist strap and heel grounders 19. Garment 20. Packaging 21. Ground cords 22. Chairs 23. PCB handing |